Non invasive ventilation - Noninvasive ventilation
Noninvasive ventilation
It will reduce the pressure of work on your lungs and you will not require tracheostomy or endotracheal intubation.
Some of the more common causes of type I and type II respiratory failure are shown in the table below: Type I respiratory failure Type II respiratory failure Pneumonia Atelectasis Pulmonary embolism Acute pulmonary oedema High altitude Acute respiratory distress syndrome Exacerbation of COPD Life-threatening asthma Obstructive sleep apnoea Extreme obesity Chest deformity e.
Usually, even after NIV is no longer required during the day, a further night of NIV is recommended.
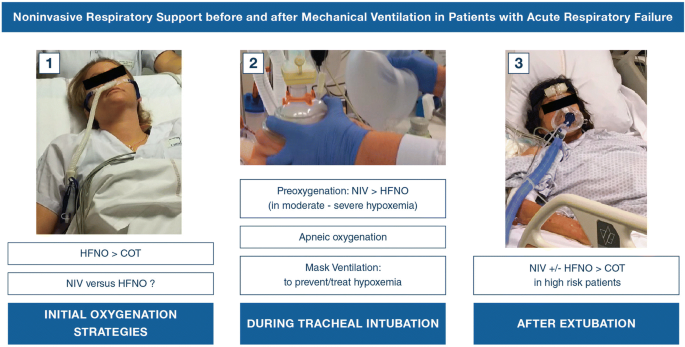
Noninvasive ventilation
This ventilation method is rarely in use these days.
It makes sure that patients get the fixed volume of tidal.
Close monitoring and serial blood gases are imperative for any patient being treated with non-invasive ventilation so any improvements or deteriorations in the clinical state can quickly be identified.
- Related articles
2022 blog.mizukinana.jp