Catecholamines - Catecholamines (Blood)

Recent Posts
- Pusat kuarantin covid jawi
- Buruj pari
- U mobile unlimited data
- Reza farzak
- Asa 3.0
- Klse focus
- Waktu subuh melaka 2021
- Ebit lew video twitter
- E operasi
- Farmasi seksyen 18
- Rupa asli org korea
- Klinik central petaling jaya
- Resepi nasi beriani guna rempah briyani
- Apam nasi sukatan cawan azie kitchen
- 5296 share price
- Son na eun
Catecholamine Definition & Meaning
We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
This results in episodic or sustained hypertension and in intermittent attacks of palpitations, cardiac arrhythmias, headache, sweating, pallor, anxiety, tremor, and nausea.
At the same time that Salter unwittingly made use of the adrenal medulla, the French physician found something unique about it.
Catecholamines (Blood)
The present work is concerned with the question whether these , besides their role as transmitters at vasomotor endings, play a part in the function of the central nervous tissue itself.
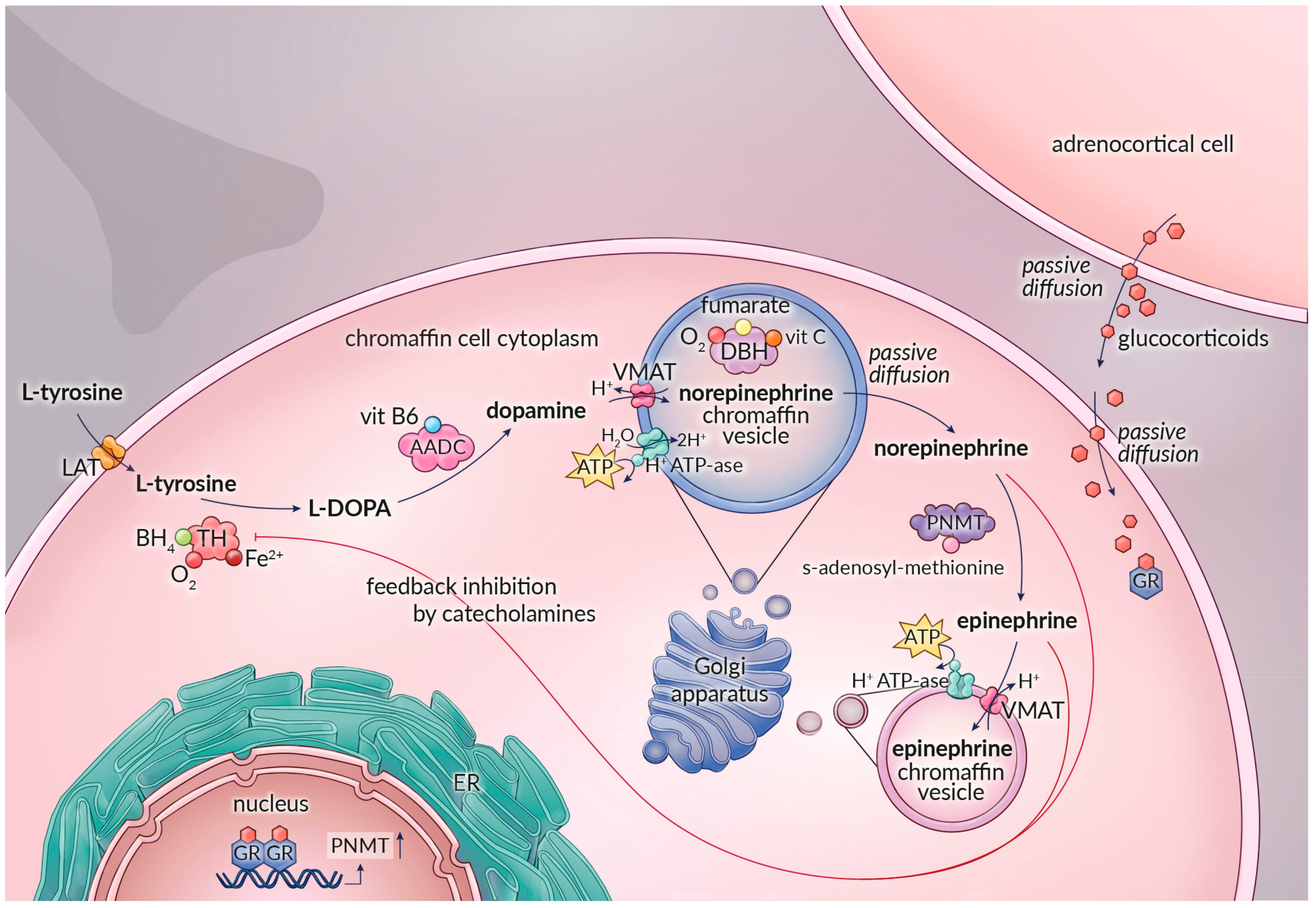
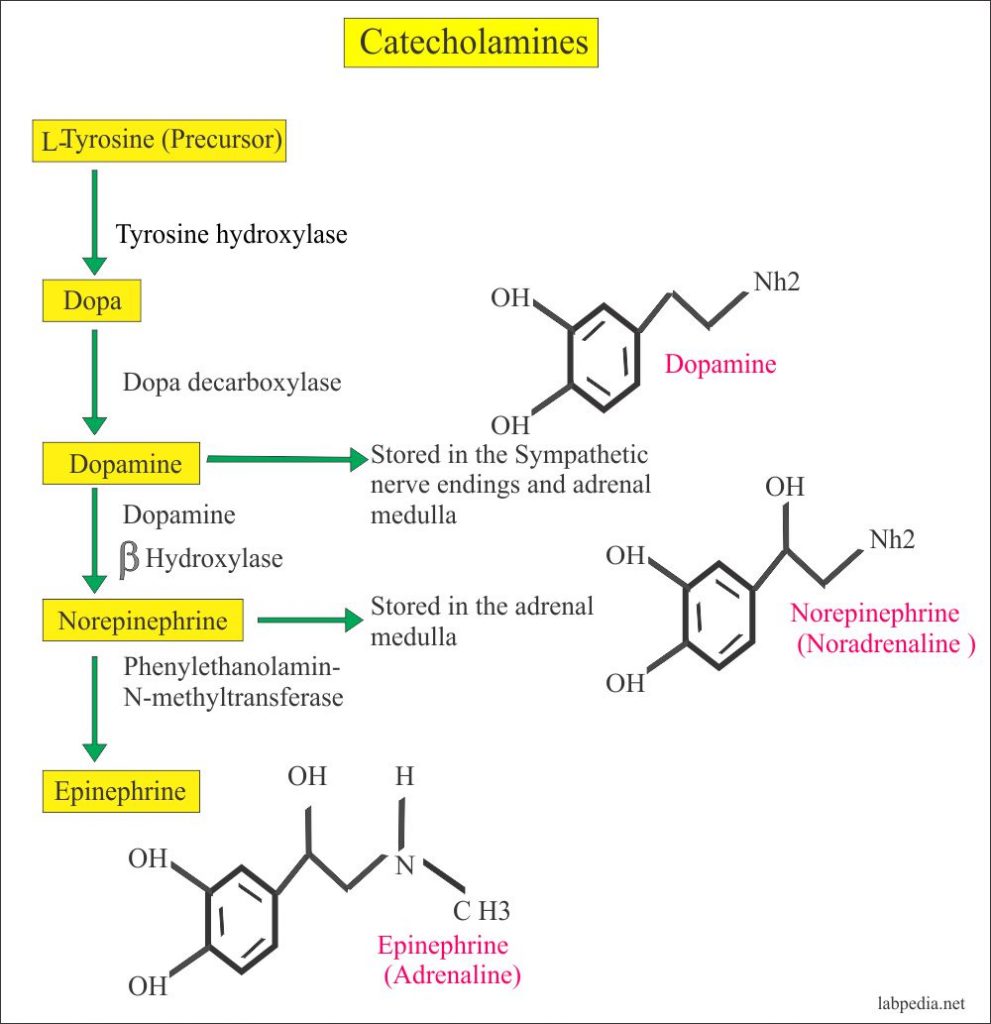
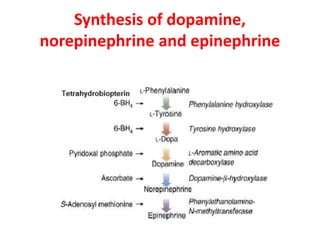
Both epinephrine and norepinephrine modulate metabolism to increase blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogenolysis in the liver via beta-2 receptors , increased glucagon secretion via beta-2 receptors and decreased insulin secretion via alpha-2 receptors from the pancreas, and lipolysis in adipose tissue via beta-3 receptors.
Lastly, Ahlquist failed to adduce the selectivity of all antagonists known at his time for the α-adrenoceptor as an additional argument.
- Related articles
2022 blog.mizukinana.jp

/GettyImages-188057931-5662310b3df78ce16196edf0.jpg)